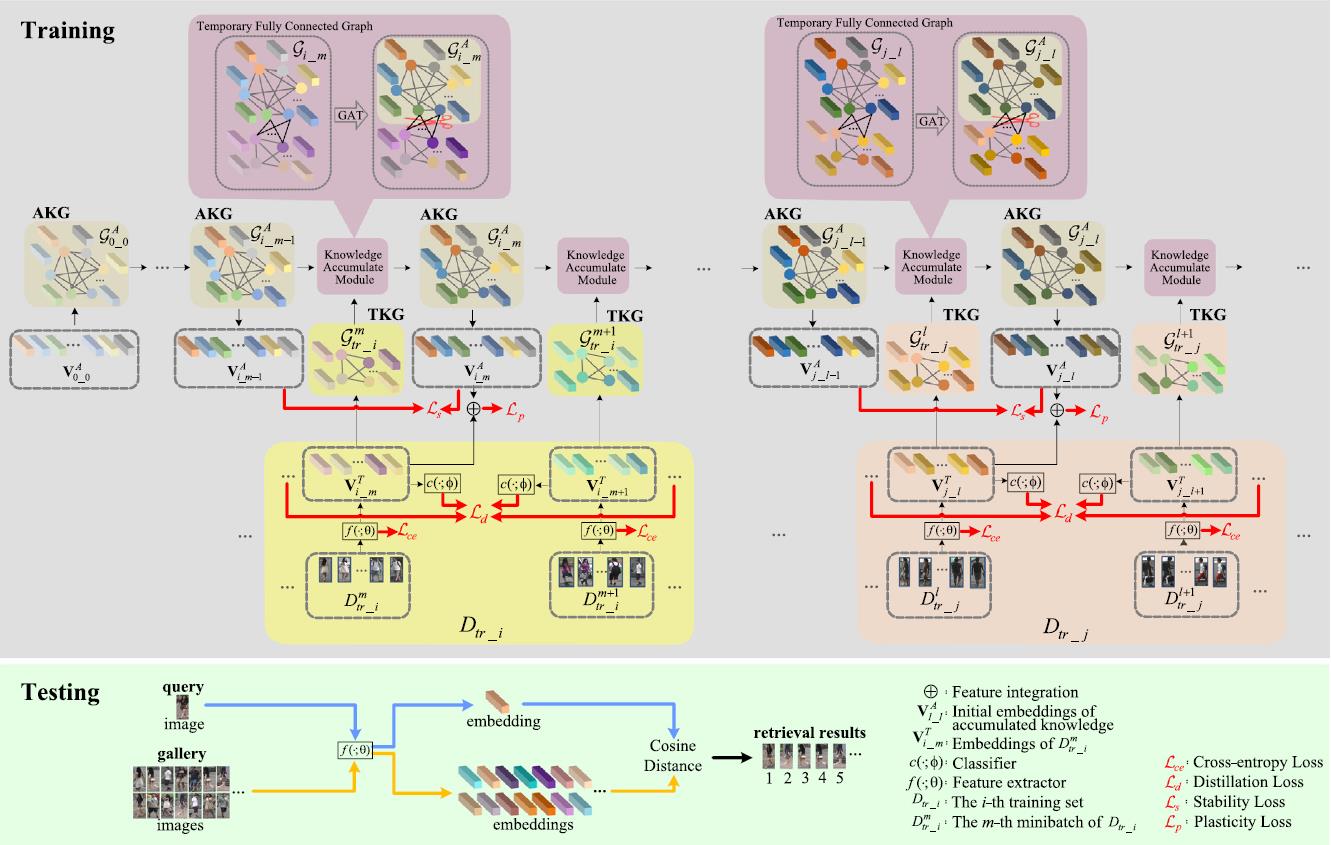
- A fully connected graph is constructed to preserve knowledge extracted from continual learning process and used to guide training.
- A temporary graph, which is also fully connected, is constructed by features extracted from any given training batch.
- The most related knowledge is propagated from the temporary graph to the knowledge preserving graph via a Graph Attention Network (GAT).
- More detials please see our paper.
- The code is available at ContinualReID.
Knowledge-Preserving continual person re-identification using Graph Attention Network
Person re-identification aims to retrieve a given person (query) from a large number of candidate images (gallery). Existing deep learning-based methods usually train the model on a fixed scenario (domain). During inference, features of the query and gallery are extracted by the trained model. The similarity between query and gallery features is then measured by Euclidean or cosine distance to match the query from the gallery.
Motivation
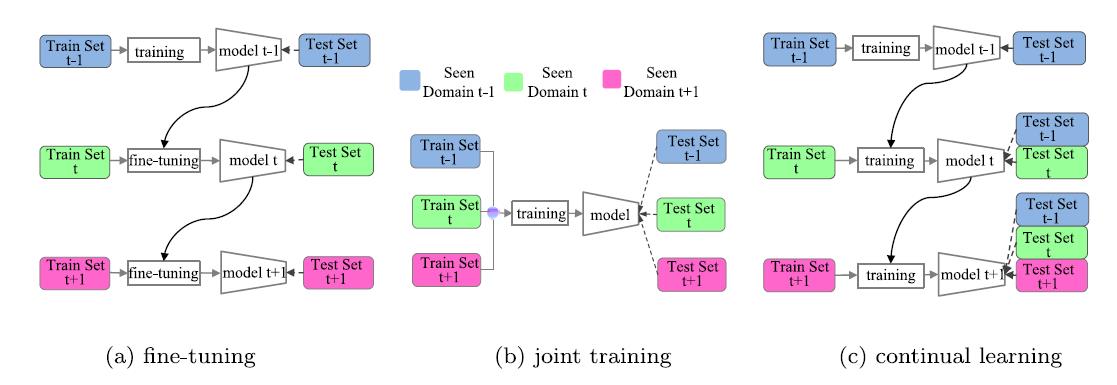
However, as the application scenario changes, which is actually the common case, the models will not perform well if it is deployed directly on these changed domains which are also called new domains. A straight-forward solution is fine-tuning the models following the schematic diagram given in Fig. 1(a). But fine-tuning on images from additional domains leads to catastrophic forgetting, namely the models will perform badly on original domains. Joint training is effective to battle against this problem, but it has to be ensured that images from all the domains are accessible at the same time as shown in Fig. 1(b), which is unrealistic in most scenarios. Continual learning aims to gradually learn a model as the image domain changes as in Fig. 1(c). The effectiveness of the model in original domains is well maintained without accessing original images. Nevertheless, the continual learning paradigm still needs to meet the challenge of catastrophic forgetting of learned knowledge on original domains.
Our Contributions
To address the above challenges, we propose a Continual person re-identification model via a Knowledge-Preserving (CKP) mechanism. Our contributions are summarized as follows:
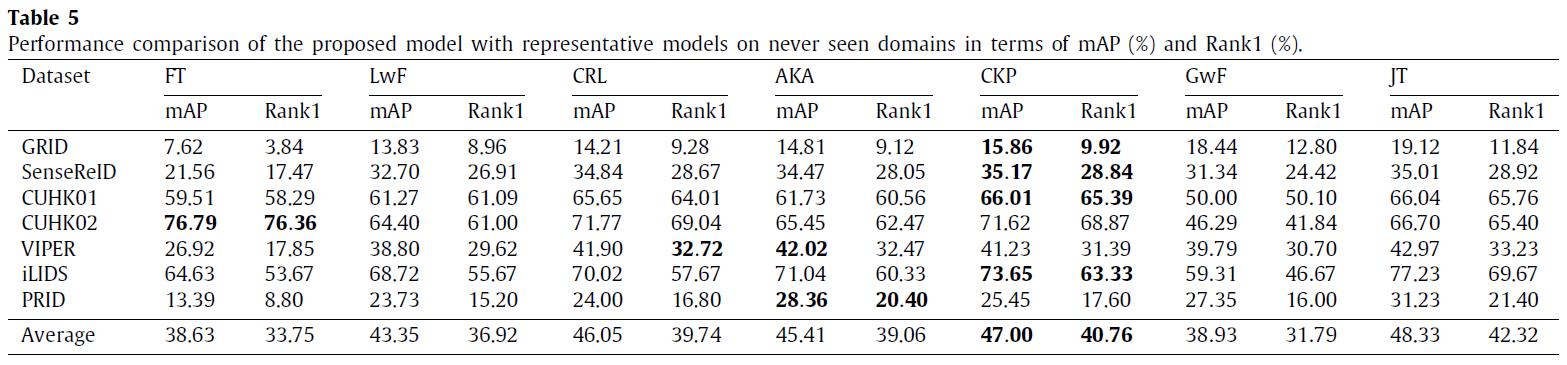
Experiments
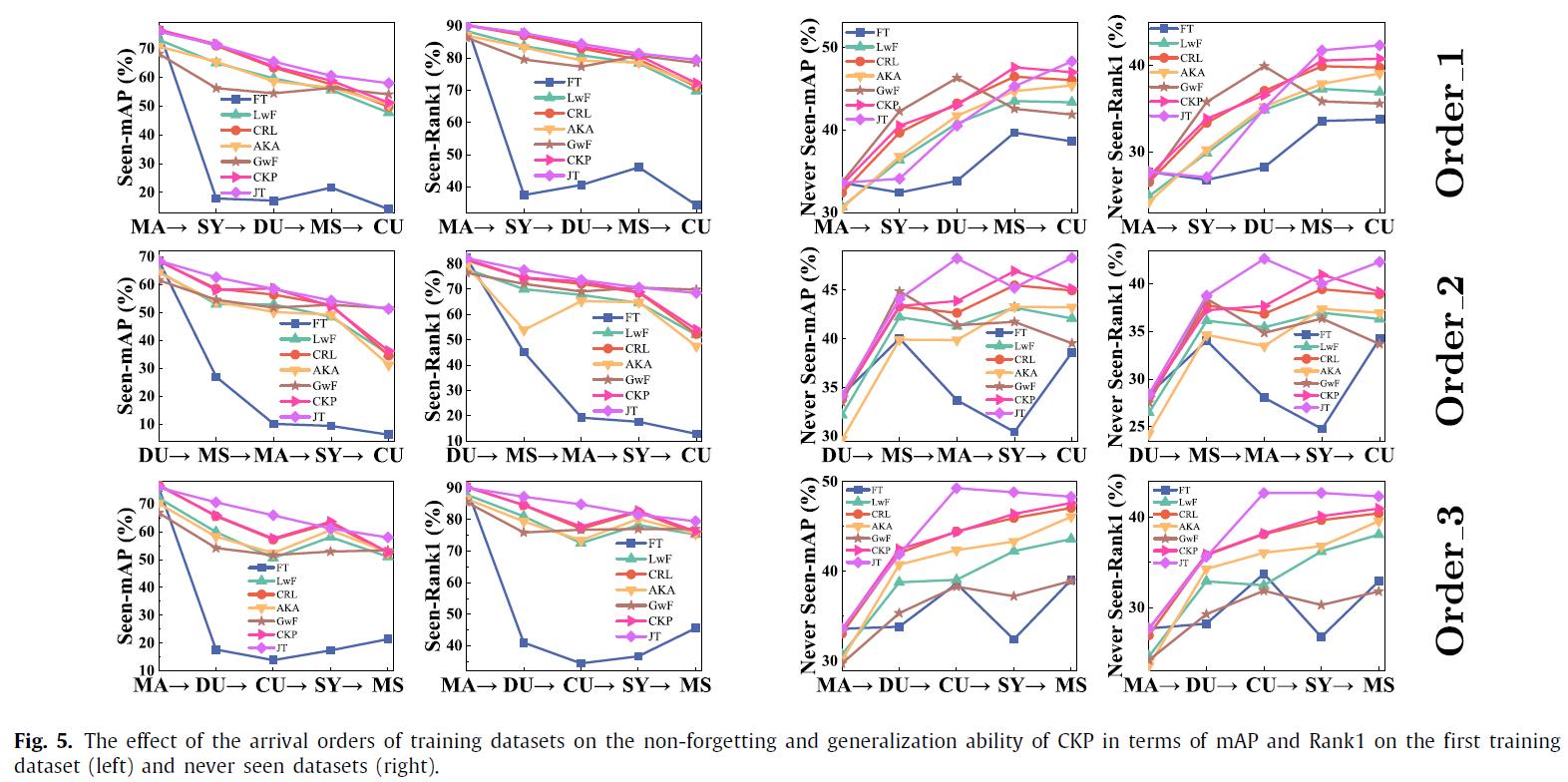
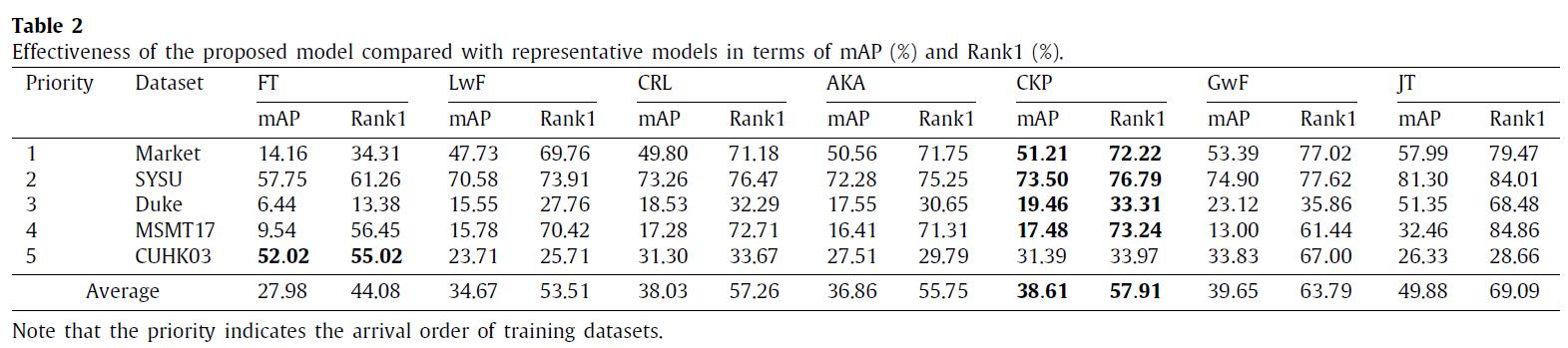
We have conducted experiments on 12 benchmark datasets of person re-identification (Market1501, DukeMTMC, CUHK03, CUHK-SYSU, MSMT17, GRID, SenseReID, CUHK01, CUHK02, VIPER, iLIDS, and PRID). Datasets are downloaded from Torchreid_Dataset_Doc and DualNorm. The comparative models include Fine-Tune (FT), Learning without Forgetting (LwF), Continual Representation Learning (CRL), Adaptive Knowledge Accumulation (AKA), Generalizing without Forgetting (GwF) and Joint Training (JT). We adopt commonly used evaluation metrics, namely the Rank-1 index and the mean average precision (mAP) to evaluate the performance of our CKP.
Sources
Citation: The author who uses this code is defaultly considered as agreeing to cite the following reference @article{liu2023knowledge, title={Knowledge-Preserving continual person re-identification using Graph Attention Network}, author={Liu, Zhaoshuo and Feng, Chaolu and Chen, Shuaizheng and Hu, Jun}, journal={Neural Networks}, volume={161}, pages={105--115}, year={2023}, publisher={Elsevier} }